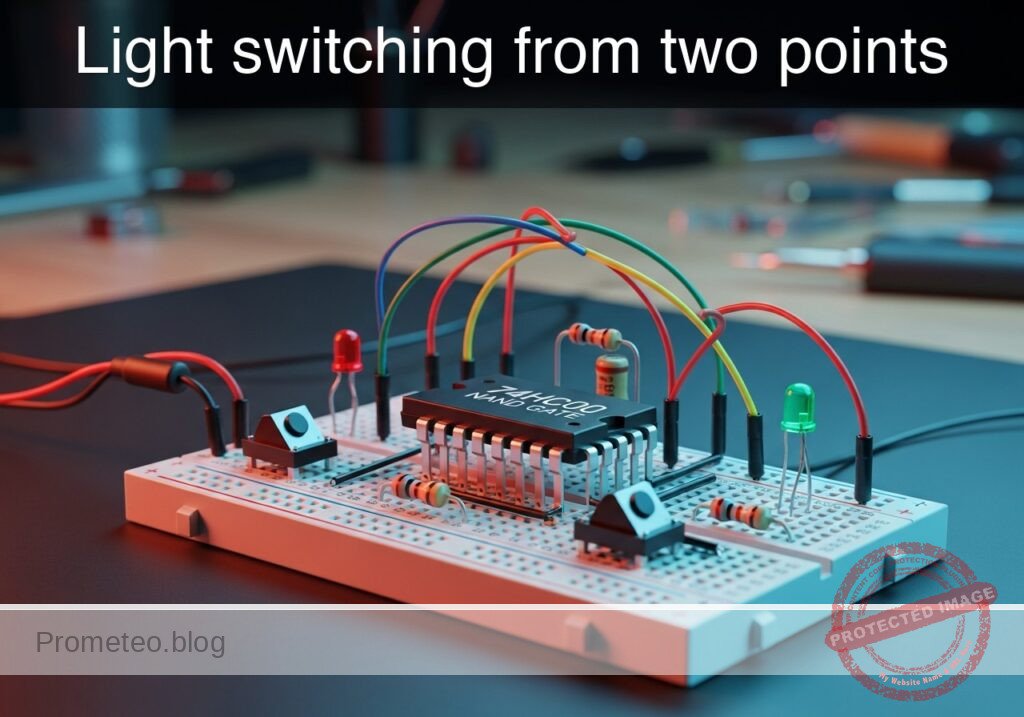
Level: Medium. Implement an XOR logic function using universal NAND gates to control a light source from two independent locations.
Objective and use case
In this case, you will build a digital logic circuit that replicates a residential 2-way switching system (hallway light) using a single 74HC00 Quad NAND Gate IC. By combining four NAND gates, you will synthesize the Exclusive-OR (XOR) function, proving that NAND gates are «universal» building blocks.
Why it is useful:
* Residential wiring simulation: Demonstrates how two switches can independently toggle a single load (hallway/staircase logic).
* Digital Logic Synthesis: Teaches how to build complex logic (XOR) from basic universal gates (NAND).
* Arithmetic Circuits: This specific XOR topology is the fundamental component of a digital «Half-Adder» used in CPU ALUs.
* Error Detection: XOR logic is used to calculate parity bits for data transmission.
Expected outcome:
* State 00: When both switches are OFF, the LED is OFF.
* State 01/10: When only one switch is ON, the LED is ON (High logic level > 3.5 V).
* State 11: When both switches are ON, the LED is OFF.
* Universality: Successful demonstration that 4 NAND gates = 1 XOR gate.
Target audience: Electronics students and hobbyists familiar with basic logic gates.
Materials
- V1: 5 V DC power supply, function: Main circuit power.
- U1: 74HC00, function: Quad 2-input NAND gate IC.
- S1: SPST Switch, function: Input A (Switch 1).
- S2: SPST Switch, function: Input B (Switch 2).
- R1: 10 kΩ resistor, function: Pull-down for Input A.
- R2: 10 kΩ resistor, function: Pull-down for Input B.
- R3: 330 Ω resistor, function: LED current limiting.
- D1: Red LED, function: Output indicator (Light).
Pin-out of the IC used
Selected Chip: 74HC00 (Quad 2-Input NAND Gate)
| Pin | Name | Logic Function | Connection in this case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 A | Input Gate 1 | Connect to Node INPUT_A |
| 2 | 1B | Input Gate 1 | Connect to Node INPUT_B |
| 3 | 1Y | Output Gate 1 | Internal Node NAND_1_OUT |
| 4 | 2 A | Input Gate 2 | Connect to Node INPUT_A |
| 5 | 2B | Input Gate 2 | Connect to Node NAND_1_OUT |
| 6 | 2Y | Output Gate 2 | Internal Node NAND_2_OUT |
| 7 | GND | Ground | Connect to Node 0 (GND) |
| 8 | 3Y | Output Gate 3 | Internal Node NAND_3_OUT |
| 9 | 3 A | Input Gate 3 | Connect to Node NAND_1_OUT |
| 10 | 3B | Input Gate 3 | Connect to Node INPUT_B |
| 11 | 4Y | Output Gate 4 | Connect to Node FINAL_OUT |
| 12 | 4 A | Input Gate 4 | Connect to Node NAND_2_OUT |
| 13 | 4B | Input Gate 4 | Connect to Node NAND_3_OUT |
| 14 | VCC | Power Supply | Connect to Node VCC (+5 V) |
Wiring guide
- V1: Connect positive terminal to node
VCCand negative terminal to node0. - U1 (Power): Connect Pin 14 to
VCCand Pin 7 to0. - S1: Connect one side to
VCCand the other to nodeINPUT_A. - R1: Connect between node
INPUT_Aand node0. - S2: Connect one side to
VCCand the other to nodeINPUT_B. - R2: Connect between node
INPUT_Band node0. - U1 (Gate 1): Connect Pin 1 to
INPUT_A, Pin 2 toINPUT_B. Pin 3 is nodeNAND_1_OUT. - U1 (Gate 2): Connect Pin 4 to
INPUT_A, Pin 5 toNAND_1_OUT. Pin 6 is nodeNAND_2_OUT. - U1 (Gate 3): Connect Pin 10 to
INPUT_B, Pin 9 toNAND_1_OUT. Pin 8 is nodeNAND_3_OUT. - U1 (Gate 4): Connect Pin 12 to
NAND_2_OUT, Pin 13 toNAND_3_OUT. Pin 11 is nodeFINAL_OUT. - R3: Connect between node
FINAL_OUTand the Anode of D1. - D1: Connect the Cathode to node
0.
Conceptual block diagram
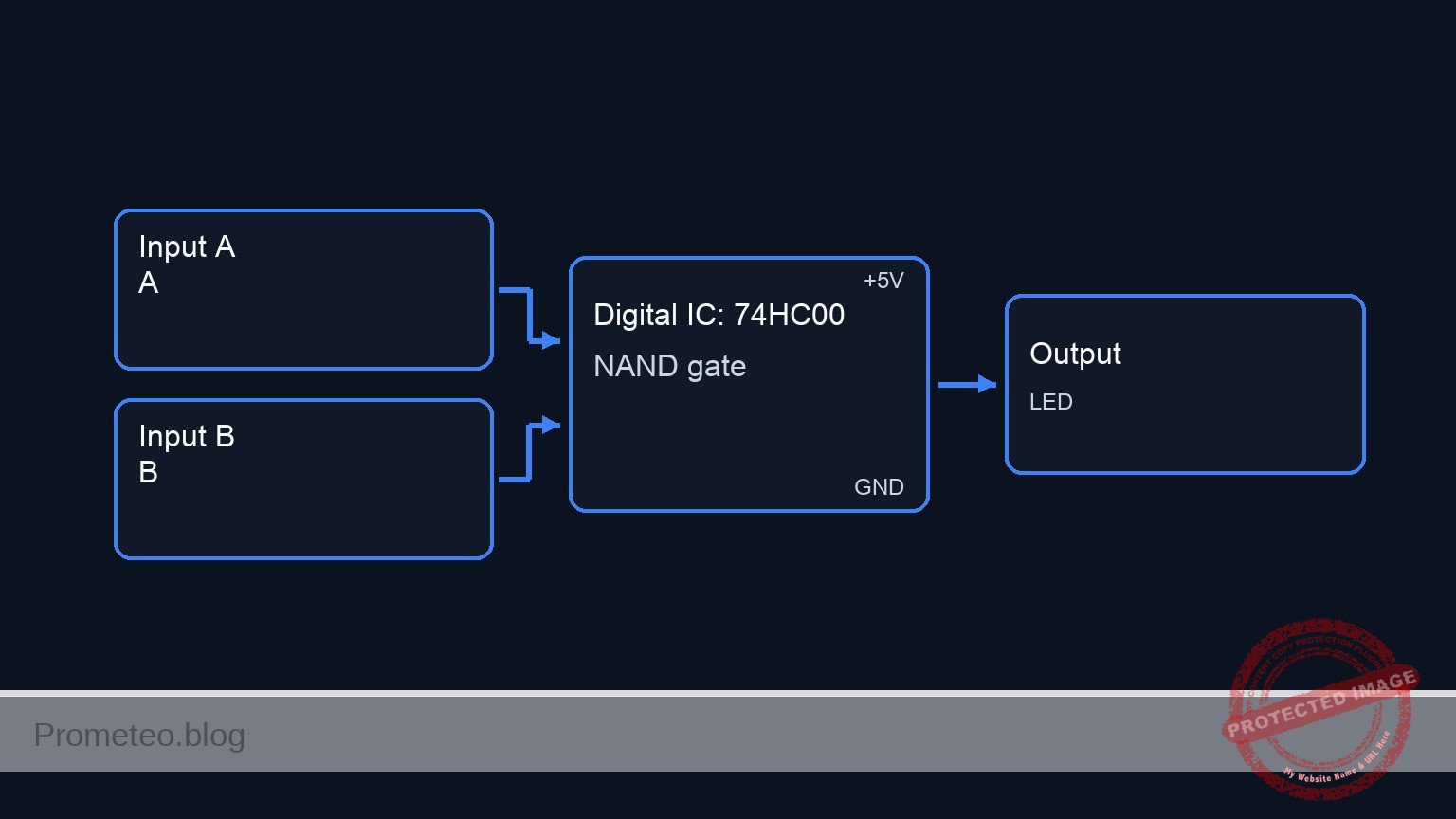
Schematic
Title: Practical case: Light switching from two points (XOR Logic)
INPUT STAGE LOGIC PROCESSING (74HC00) OUTPUT STAGE
(User Controls) (NAND-based XOR Circuit) (Indicator)
(Pin 4)
VCC --> [ S1 ] --(Node A)----------> [ U1:Gate 2 ] --(NAND_2)--\
| (Pin 5,6) \
[ R1 ] ^ \
v | \
GND (NAND_1_OUT) \
| \
| \
(Node A) & (Node B) -----------> [ U1:Gate 1 ] --> [ U1:Gate 4 ] --(FINAL)--> [ R3 ] --> [ D1: LED ] --> GND
(Pin 1,2->3) / (Pin 12,13->11)
| /
| /
(NAND_1_OUT) /
^ | /
[ R2 ] v /
| (Pin 9) /
VCC --> [ S2 ] --(Node B)----------> [ U1:Gate 3 ] --(NAND_3)-/
(Pin 10,8)
Truth table (Synthesized XOR)
| Switch A (S1) | Switch B (S2) | LED State (D1) | Logic Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (OFF) | 0 (OFF) | OFF (0) | No active input |
| 0 (OFF) | 1 (ON) | ON (1) | Inputs differ |
| 1 (ON) | 0 (OFF) | ON (1) | Inputs differ |
| 1 (ON) | 1 (ON) | OFF (0) | Inputs match |
Measurements and tests
- Initial State Check: Ensure both S1 and S2 are open. Measure voltage at Pin 11 (
FINAL_OUT). It should be < 0.5 V (Logic 0). D1 should be dark. - First Switch Toggle: Close S1 only. Measure voltage at Pin 11. It should be close to 5 V (Logic 1). D1 should light up.
- Second Switch Toggle: Open S1 and close S2. Observe D1. It should light up again (Logic 1).
- Collision Check: Close both S1 and S2 simultaneously. Measure voltage at Pin 3 (
NAND_1_OUT). Since both inputs are High, Pin 3 must be Low. Consequently, Pin 11 (FINAL_OUT) should go Low, turning D1 OFF.
SPICE netlist and simulation
Reference SPICE Netlist (ngspice)
* Practical case: Light switching from two points
* Title: Light switching from two points
* ==============================================================================
* COMPONENT MODELS
* ==============================================================================
* Simple LED Model
.model DLED D(IS=1e-22 RS=10 N=1.5 CJO=10p BV=5 IBV=10u)
* Voltage Controlled Switch Model for Buttons
* Vt=2.5V threshold, Ron=1 ohm, Roff=10Meg ohm
.model SW_PUSH SW(Vt=2.5 Ron=1 Roff=10Meg)
* ==============================================================================
* MAIN CIRCUIT
* ==============================================================================
* --- Power Supply ---
* V1: 5 V DC power supply
* ... (truncated in public view) ...Copy this content into a .cir file and run with ngspice.
Simulation Results (Transient Analysis)
Show raw data table (773 rows)
Index time v(input_a) v(input_b) v(final_out) v(led_node) 0 0.000000e+00 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 -1.32951e-36 1 1.000000e-08 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 -3.37339e-37 2 2.000000e-08 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 1.661518e-37 3 4.000000e-08 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 2.976605e-37 4 8.000000e-08 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 8.146600e-38 5 1.600000e-07 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 -2.74917e-38 6 3.200000e-07 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 -1.00046e-38 7 3.562500e-07 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 -9.54478e-40 8 4.196875e-07 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 1.440911e-39 9 4.372461e-07 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 5.873353e-40 10 4.679736e-07 4.995005e-03 4.995005e-03 -3.70921e-68 -1.64244e-40 11 5.019934e-07 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 5.471353e-16 12 5.700330e-07 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 1.883035e-16 13 7.061121e-07 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 -1.89304e-16 14 9.782703e-07 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 1.713539e-16 15 1.000000e-06 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 -8.76370e-17 16 1.043459e-06 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 2.969253e-18 17 1.130378e-06 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 1.336375e-17 18 1.304216e-06 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 1.285658e-18 19 1.651892e-06 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 -4.38731e-19 20 2.347244e-06 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 -3.76487e-20 21 3.347244e-06 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 3.641502e-21 22 4.347244e-06 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 3.034717e-22 23 5.347244e-06 4.999500e+00 4.999500e+00 -3.70921e-68 -2.04956e-23 ... (749 more rows) ...
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
- Floating Inputs: Forgetting R1 or R2 causes the inputs to «float,» often reading as High due to electromagnetic noise. Solution: Always ensure inputs are pulled to Ground when the switch is open.
- Incorrect Gate Feedback: Wiring Pin 3 output to the wrong inputs on Gates 2 or 3 destroys the logic. Solution: Double-check that the output of the first NAND (Pin 3) connects to BOTH the second (Pin 5) and third (Pin 9) gates.
- Forgetting Power: Logic chips do not work passively. Solution: Verify 5 V on Pin 14 and continuity to Ground on Pin 7 before inserting signals.
Troubleshooting
- Symptom: LED is always ON, regardless of switch position.
- Cause: Wiring error at the final NAND gate (Gate 4) or output shorted to VCC.
- Fix: Check connections at Pins 11, 12, and 13. Ensure Pin 11 is not touching the positive rail.
- Symptom: LED behaves like an OR gate (stays ON when both switches are ON).
- Cause: The first NAND gate (Gate 1) is not effectively inhibiting the signal.
- Fix: Check continuity on Pins 1, 2, and 3. If Gate 1 output stays High when inputs are High, the XOR logic fails.
- Symptom: Circuit works erratically when touching the wires.
- Cause: Missing pull-down resistors (floating inputs).
- Fix: Verify R1 and R2 are securely connected between the input pins and Ground.
Possible improvements and extensions
- 3-Way Switching: Add a third switch and another XOR stage (using a second 74HC00 or a 74HC86) to control the light from three locations.
- Comparison with Dedicated IC: Build the same circuit using a 74HC86 (Quad XOR) alongside this one to compare propagation delay and wiring complexity.
More Practical Cases on Prometeo.blog
Find this product and/or books on this topic on Amazon
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If you buy through this link, you help keep this project running.